Elephant Reserves in India & Project Elephant
Elephant Reserves in India
Table of Contents
What is Elephant Reserves?
· Elephant Reserves and Elephant Corridors are the special Facilities which are developed under the Specialized Conservation Program for Elephant – Project Elephant. The Project Elephant was launched in 1992 by the Central Government of India.
· The area of habitation where the elephants are found primarily, fall under Elephants Reserves, which helps in conservation of the species as well as preserve their natural habitat.
· The Indian elephant Elephas maximus occurs in the central and southern Western Ghats, North-east India, eastern India and northern India and in some parts of southern peninsular India.
· Elephants are included in Schedule I of the Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 and in Appendix I of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Flora and Fauna (CITES). It occurs in 16 of the 28 states in the country and is showing an increasing trend across its distributional range.

Elephant as the National Heritage Animal of India
· The elephant has been declared as the national heritage animal by the government of India in 2010 after the recommendations of the standing committee on national board for wildlife. This was to ensure sufficient protection for elephants before its number fall to panic levels as it had happened in case of tigers.
· A proposed National elephant conservation authority (NECA) on the lines with NTCA has been proposed to be constituted by amending the Wildlife Protection Act 1972.
Project Elephant
· Project Elephant was launched in 1992 by the Government of India under Ministry of Environment and Forests to provide financial and technical support of wildlife management efforts by states for their free ranging populations of wild Asian Elephants.
· In our country there are approximately 30 thousand elephants spread in 16 Elephant states. Maximum number of elephants is in Kerala, followed by Karnataka and Assam.
· It is a centrally sponsored scheme to assist the States on three key areas –
o Protection of wild elephants, their habitat and corridors
o Address the issue of man – animal conflict and
o welfare of domesticated elephants
· The Project is being mainly implemented in 13 States/UTs, viz. Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Kerala, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Orissa, Tamil Nadu, Uttaranchal, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal. Small support is also being given to Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh.
· States are being given financial as well as technical assistance in achieving the objectives of the Project.
Objectives of Project Elephant
· To assist states having populations of wild elephants and to ensure long term survival of identified viable populations of elephants in their natural habitats.
· To mitigate and prevent the increasing conflict between humans and elephants in elephant habitats. It also aims to reduce and remove the pressure of human and domestic livestock grazing and other activities in important elephant habitat.
· To ensure ecological restoration of the natural elephant habitats and their migratory routes.
· To promote scientific research on issues related to conservation of elephants and promotion of public awareness and education on these issues.
· To ensure the proper health care and breeding of domesticated elephants. To facilitate veterinary care and Eco-development for the elephants.
· Developing scientific and planned management measures for conservation of elephants.
· Protecting the elephants from poachers, preventing illegal ivory trade and other unnatural causes of death.
Main Activities of Project Elephant
· Ecological restoration of existing natural habitats and migratory routes of elephants;
· Development of scientific and planned management for conservation of elephant habitats and viable population of Wild Asiatic elephants in India;
· Promotion of measures for mitigation of man elephant conflict in crucial habitats and moderating pressures of human and domestic stock activities in crucial elephant habitats;
· Strengthening of measures for protection of Wild elephants form poachers and unnatural causes of death;
· Research on Elephant management related issues;
· Public education and awareness programmes;
· Eco-development
· Veterinary care
· Elephant Rehabilitation/Rescue Centers
Elephant Reserves in India
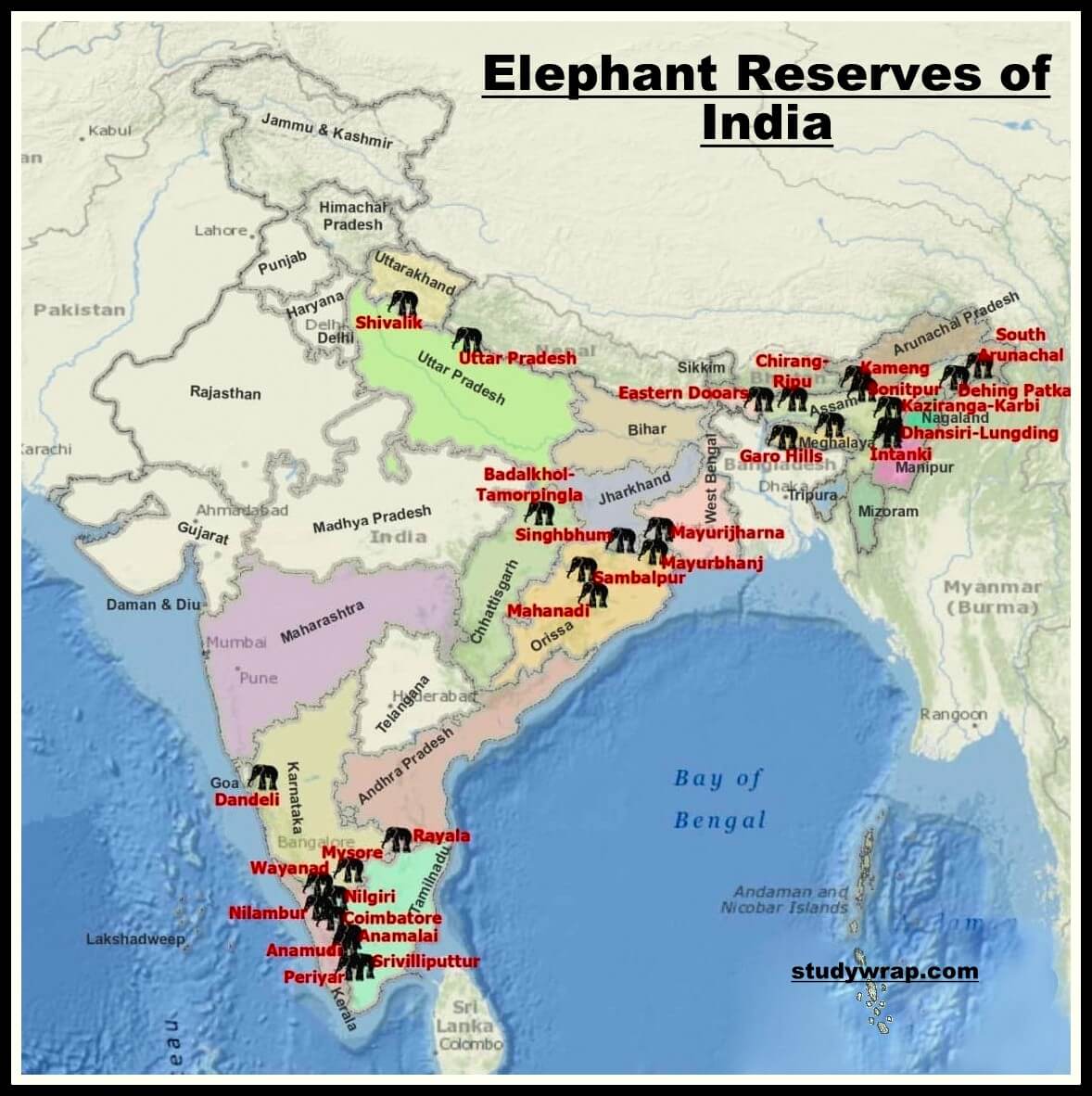
· A total of 32 Elephant Reserves in India covering 58000 km² have been so far notified in India by the Central and state governments.
· They cover not only the forest patches of different kinds but also villages, townships, agricultural land, tea plantations and revenue land.
· Sighbhum Elephant Reserve in Jharkhand was the first reserve to be notified in 2001. Out of 32 Elephant Reserves in India, maximum number is in Assam and Odisha with five each.
· As of 2010, 32 Elephant Reserves extending over about 58,000 sq. km have been formally notified by various State Governments.
Complete State-wise List of Elephant Reserves in India
· The list of Elephant Reserves in India with area is as follows –
|
Range |
State |
Reserve Name |
Estd. |
Area (km²) |
|
East-Central
|
West Bengal |
Mayurjharna |
2002 |
414 |
|
Jharkhand |
Singhbhum |
2001 |
4,530 |
|
|
Orissa |
Mayurbhanj |
2001 |
3,214 |
|
|
Orissa |
Sambalpur |
2002 |
427 |
|
|
Orissa |
Baitarni |
|
1,755 |
|
|
Orissa |
South Orissa |
|
1,049 |
|
|
Chhattisgarh |
Lemru |
|
450 |
|
|
Chhattisgarh |
Badalkhol-Tamorpingla |
|
4,216 |
|
|
Kameng-Sonitpur |
Arunachal Pradesh |
Kameng |
2002 |
1,892 |
|
Assam |
Sonitpur |
2003 |
1,420 |
|
|
Eastern-South |
Assam |
Dihing-Patkai |
2003 |
937 |
|
Arunachal Pradesh |
South Arunachal |
|
900+ |
|
|
Kaziranga
|
Assam |
Kaziranga-Karbi Anglong |
2003 |
3,270 |
|
Assam |
Dhansiri-Lungding |
2003 |
2,740 |
|
|
Nagaland |
Intanki |
2005 |
202 |
|
|
North Bengal- Greater Manas |
Assam |
Chirang-Ripu |
2003 |
2,600 |
|
West Bengal |
Eastern Dooars |
2002 |
978 |
|
|
Meghalaya |
Meghalaya |
Garo Hills |
2001 |
3,500 |
|
Meghalaya |
Khasi Hills |
|
1,331 |
|
|
Brahmagiri-Nilgiri- Eastern Ghats
|
Karanataka |
Mysore |
2002 |
6,724 |
|
Kerala |
Wayanad |
2002 |
1,200 |
|
|
Tamil Nadu |
Nilgiri |
2003 |
4,663 |
|
|
Andhra Pradesh |
Rayala |
2003 |
766 |
|
|
Kerala |
Nilambur |
2002 |
1,419 |
|
|
Tamil Nadu |
Coimbatore |
2003 |
566 |
|
|
Anamalai-Nelliampathy-High Range |
Tamil Nadu |
Anamalai |
2003 |
1,457 |
|
Kerala |
Anamudi |
2002 |
3,728 |
|
|
Periyar-Agasthyamalai |
Kerala |
Periyar |
2002 |
3,742 |
|
Tamil Nadu |
Srivilliputhur |
2003 |
1,249 |
|
|
North-Western |
Uttarakhand |
Shivalik |
2003 |
5,405 |
|
Uttar Pradesh |
Uttar Pradesh |
2009 |
744 |
|
|
Total |
|
|
|
69,583 |
Elephant Corridor
· Elephant corridor is the narrow strips of forested lands which connects larger elephant habitats with significant elephant populations. It acts as a conduit for the movement of elephants between the elephant habitat. It is necessary to enhance species survival and birth rate of the elephant population in the wild.
· There are around 88 elephant corridors in India out of which 20 are in South India, 12 in North Western India, 14 in North West Bengal, 20 in Central India and 22 in North Eastern India. About 77.3% of these corridors are regularly used by the elephants.
· One-third of these corridors are of high ecological priority and other two third are of medium priority.
· These elephant habitats are facing threats due to their fragmentation. This problem is severe in areas of Northern West Bengal followed by North Western India, North Eastern India and Central India. This fragmentation was least in South India.
Threats to Elephant Corridors
· Habitat loss leading to fragmentation and destruction caused by developmental activities like construction of buildings, roads, railways, holiday resorts and the fixing solar energized electric fencing, etc. This often results in conflicts with humans, due to elephants raiding or destroying crops.
· Mining activities such as coal mining and iron ore mining have been described as single biggest threats to elephant corridor in Central India.
· Orissa, Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh, are mineral-rich states, but also have the highest number of elephant corridors in the country, which makes them known for elephant-man conflicts.
· There is also a serious poaching problem, as elephant ivory from the tusks is extremely valuable.
· Elephants need extensive grazing grounds and most reserves cannot accommodate them. If protected areas are not large enough, elephants may search for food elsewhere.
Monitoring of Illegal Killing of Elephants (MIKE) Program
· Mandated by COP resolution of CITES, MIKE program started in South Asia in the year 2003 with following purpose:
o To provide information needed for elephant range States to make appropriate management and enforcement decisions, and to build institutional capacity within the range States for the long-term management of their elephant populations.
· The main objective of MIKE program are –
o To measure levels and trends in the illegal hunting of elephants;
o To determine the factors which are responsible for such changes, and to assess in particular about the impact of decisions of the conference of parties to CITES responsible for such changes.
o To determine the factors causing or associated with such changes, and to try and assess in particular to what extent observed trends are a result of any decisions taken by the Conference of the Parties to CITES.
For more Details on PROJECT ELEPHANT – Click Here.
So, this was all about the Complete State-wise List of Elephant Reserves in India and Project Elephant and Elephant Corridors. If you want to read more about Project Elephant, then Click Here – PROJECT ELEPHANT.
If you find this article useful, than do share it with your friends and family and do like our Facebook Page to get regular updates.

