Principles of Ecology and its Fundamental Concepts
Principles of Ecology and its Fundamental Concepts
Table of Contents
There are some fundamental Principles of Ecology that describes various characteristics of living organisms such as evolution and distribution of plants and animals, extinction of species, consumption and transfer of energy in different components of biological communities, cycling and recycling of organic and inorganic substances, interactions and inter relationships among the organisms and between organisms and physical environment etc.
Some Basic Principles of Ecology
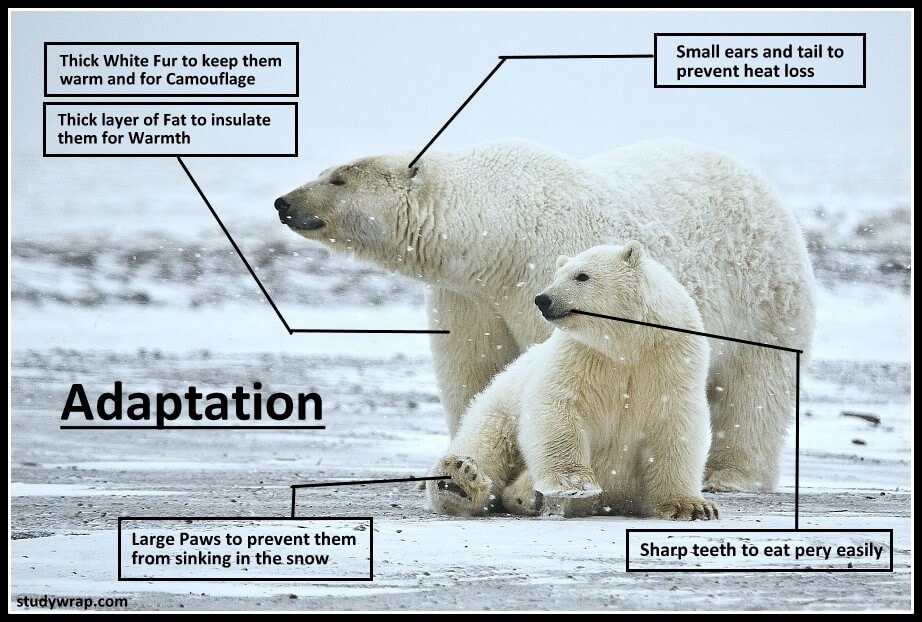
Adaptation
-
- An adaptation is, “the appearance or behaviour or structure or mode of life of an organism that allows it to survive in a particular environment”.
- In other words, Adaptations refer to how a species has changed to be able to fit into its environment and use its environments resources.
- Adaptations have a genetic basis and have been evolved and perfected through the evolutionary process.
Types of Adaptation
-
-
- Adaptation may be –
- Morphological – when trees grew higher, the giraffe’s neck got longer;
- Physiological – snakes produce poisonous venom to ward off predators and to capture prey;
- Behavioural – animals migrating temporarily to a less stressful habitat.
- Adaptation may be –
-
Some Examples of Adaptation
-
-
- Desert plants have a thick cuticle on their leaf surfaces and have their stomata arranged in deep pits to minimise water loss through transpiration.
- Some desert plants like Cactus, have no leaves as they are reduced to spines, and the photosynthetic function is taken over by the swollen stem.
- Shape of bird’s beak suited to the kind of food it needs to procure.
- Presence of feathers and wings in birds for movement in air.
- Mammals from colder climates generally have shorter ears and limbs to minimise heat loss.
-
Variation
-
- Variations are induced by changes in genetic makeup due to addition or deletion of certain genes. Variations are produced as a result of chance mutation.
- Mutations, change in climate, geographical barriers induce variations over a period of time.
- The difference in the colour of skin, type of hair; curly or straight, eye colour, blood type among different ethnic groups represents variation within human species.
- Competition and natural selection determines as to which variation will succeed and survive. Those variations that enable a species to survive in the struggle for existence are encouraged and promoted.
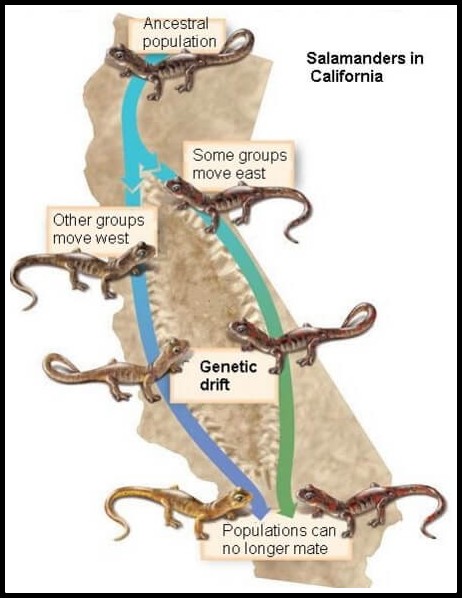
Speciation
-
- Speciation is the process by which new species are formed, and evolution is the mechanism by which speciation is brought about.
- A species comprises of many populations. Often different populations of a species remain isolated due to some geographic barrier such as mountain, ocean, river, etc.
- Geographic isolation leads to speciation between the different sub-populations.
- After a long period of time, the sub-populations become very different (genetic drift) and get isolated, reproductively, i.e. they no longer interbreed.
- Later even when the barrier is removed, the sub-populations are unable to interbreed, and thus subsequently the sub-populations become two different species.
Mutation
-
- Mutation is a process of spontaneous evolutionary change which introduces inheritable variations in species. The mutation process furnishes the raw materials for evolution.
- Further, in a sexually reproducing population, meiosis and fertilisation produce a new combination of genes every generation, which is termed recombination.
- Thus, members of the same species show ‘variation’ and are not identical.
Natural Selection
-
-
- Natural Selection is the mechanism proposed by Darwin and Wallace. It is the process by which species adapt to their environment.
- It is an evolutionary force that selects among variations. Such genes are reproduced more in a population due to natural selection.
- Those offsprings which are fit to their immediate environment have a better chance of survival, reaching reproductive age and passing on the suitable adaptations to their offspring.
-
Evolution
-
- Evolution is the change which gives rise to new species.
- It happens in order to make the organism better suitable to the present environment.
- Evolution involves the processes of natural selection, adaptation, variation etc.
- A valid theory of evolution was propounded by Charles Darwin and Alfred Wallace in 1859.
- This theory has been extended in the light of progress in genetics and is known as Neo-Darwinism. It has the following features:
-
-
- Organisms tend to produce more off springs that can be supported by the environment.
- Mutation causes new genes to arise in a population. Further, in a sexually reproducing population, meiosis and fertilisation produce new combination of genes every generation, which is termed Thus members of the same species show ‘variation’ and are not exactly identical. Variations are heritable.
- An evolutionary force which Darwin termed natural selection, selects among variations i.e. genes that help the organism to adopt to its environment. Such genes are reproduced more in a population due to natural selection.
- Those offspring which are suited to their immediate environment have a better chance of surviving, reaching reproductive age and passing on the suitable adaptations to their progeny.
- Evolution thus results in adaptation and diversity of the species.
-
Extinction
-
- Extinction is generally a natural occurrence. It means the dying out of a variety or a species.
- The primary reason behind extinctions is environmental change or biological competition.
- Extinction occurs when species cannot evolve fast enough to cope with the changes taking place in their environment.
- Extinction may take place due to catastrophic natural phenomena such as tsunami, volcanoes etc. In recent time, human activities such as deforestation, over exploitation, environmental pollution and environmental change are other factors responsible for extinction.
Fundamental Concepts and Principles of Ecology
Some important fundamental concepts and Principles of Ecology in terms of ecosystem may be outlined as follows –
- Ecosystem is a fundamental well-structured unit that brings physical environment and living organisms together in a single framework which facilitates the study of interactions between biotic and abiotic components and various Principles of Ecology.
- Ecosystems are functional units where in two biotic components, namely autotrophic and heterotrophic components are of major significance.
- The biotic and abiotic components of biosphere ecosystem are closely related through a series of large scale cyclic mechanisms which help in the transfer of energy, water, chemicals and sediments in various components of the biosphere.
- Sustained life on the earth is a characteristic of ecosystem.
- Natural hazards affect adversely the biological communities in general and man in particular when biological processes are associated with natural hazards, yet severe hazards are created.
- All living organisms and physical environment are mutually responsive. The varying degrees of interactions among organisms, at both inter and intraspecific levels are positive, negative and sometimes neutral.
- Solar radiation is the main driving force of the ecosystem and it is trapped by green plants through the process of photosynthesis.
- Energy flow in ecosystem is unidirectional and non-cyclic. The energy pattern and energy flow are governed by the laws of thermodynamics.
- The energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next higher trophic level but organisms at higher trophic levels receive energy from more than one trophic level. There is increase in the relative loss of energy through respiration with increasing trophic levels.
- L. Linderuan (1942) suggested some Principles of Ecology about the relationships between the trophic levels within a natural ecosystem.
-
- Principle-1 – With an increase in distance between the organisms of a given trophic level and the initial source of energy, the probability of the organisms to depend exclusively on the preceding trophic level for energy decreases.
- Principle-2 – The relative loss of energy due to respiration is progressively greater to higher trophic levels because the species at higher trophic levels being relatively larger in size have to move and work for getting food and therefore more energy is lost due to respiration.
- Principle-3 – Species at progressively higher trophic levels appear to be progressively more efficient in using their available food supply, because increased activity by predators increases their chances of encountering suitable prey species, and in general predators are less specific than their prey in food preference.
- Principle-4 – Higher trophic levels tend to be less discrete than the lower ones because the organisms at progressively higher trophic levels receive energy from more than one source and are generalists in their feeding habit and they are more efficient in using their available food.
- Principle-5 – Food-chains tend to be reasonably short. Four vertical links is a common maximum because loss of energy is progressively higher for higher trophic levels and species at higher levels tend to be less discrete.
-
- The inorganic and organic substances are circulated among the various components of biosphere through a series of closed system of cycles collectively known as Biogeochemical Cycles.
- The ecosystem productivity depends on two factors –
-
- The availability of the amount of solar radiation to the primary producers at trophic level-I.
- The efficiency of the plants to convert solar energy into chemical energy. There is marked positive correlation between primary productivity and solar radiation.
-
- There is inbuilt self-regulating mechanism in natural ecosystem, known as Homeostatic Mechanisms, through which any change caused by external factors in the ecosystem is counter balanced by the responses of the system to the change in such a way that ultimately ecosystem or ecological stability is restored. The ecological diversity and complexity enhance ecosystem stability. The ecological stability can be attained by the following manners:
-
- According to C. S. Elton (1958), increase in the diversity of food webs promotes ecosystem stability.
- According to H. MacArthur (1955), the ecosystem stability increases with increase of number of links in the food web.
- According to E.P. Odum (1971), high species diversity of a mature ecosystem representing a climax community is related to more stability of natural ecosystem.
-
- Ecosystem instability results when an ecosystem becomes unable to adjust with environmental changes.
- According to Charles Darwin (1859), evolution of species characterises the inherently dynamic nature of ecosystem.
- Darwin’s concept of progressive evolution of species was afterward challenged by Devries and a new concept of mutation was proposed. Mutation is a process of spontaneous evolutionary change which introduces inheritable variations in species. Dobzhansky ( 1950) suggested the following ideas regarding mutation –
-
- The mutation process furnishes the raw materials for evolution.
- During sexual reproduction, numerous gene patterns are produced.
- The possessors of some gene patterns have greater fitness than the possessors of other patterns in available environment.
- The frequency of superior gene patterns is increased by the process of natural selection while the inferior gene patterns are suppressed.
- Groups of some combinations of proven adaptive worth become segregated into closed genetic system, called species.
-
- The transition stages of sequential changes from one vegetation community to another vegetation community are called ‘sere’. The sere is complete when the succession of vegetation community after passing through different phases, concludes into equilibrium condition. The vegetation community developed at the end of succession is called ‘Climax vegetation’ or ‘Climax community’.
- Besides community succession, the ecosystem also undergoes the process of successional changes. There are two fundamental ideas regarding the process of successional changes.
-
- According to E.P. Odum (1962), ecological succession is one of the most important processes which results from the community modifying the environment,
- According to R. H. Whittaker (1953), the successional development of ecosystem is characterised by four major changes in the ecosystem –
- Progressive increase in the complexity and diversity of community;
- Progressive increase in the structure and productivity of the ecosystem;
- Increase in soil maturity;
- Increase in relative stability and regularity of populations within the ecosystem and stability of the ecosystem itself.
-
- The ecosystem is mainly modified by man through the exploitation of natural resources. Man reduces ecological diversity and complexity by removing a host of biotic communications.
- Preserving diversity in a world of rapidly shrinking resources will require a prompt and universal response on an appropriate application of ecological knowledge.
So, this was all about the Principles of Ecology and Fundamental Concepts of Ecology.
In the Next Post (Click Here), we will discuss about the Function of Ecosystem – Food Chain & Food Web.