Cell – Fundamental Unit of Life (Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic cell)
Cell – Fundamental Unit of Life
Table of Contents
What is Cell ?
- The Cell is defined as –
“A unit of biological activity delimited by a deferentially permeable and capable of self reproduction in a medium free of other living system.”
- Cell is Basic Structural and Functional Unit of Living Organism.
- All organism are made up of Cells.
- These cell performs all the activities required for the sustainance of life.
Discoveries Related to Cell
Robert Hooke (1665) – studied the cell thin slice of Bottle Cork and found small compartment like structure which he called as Cells.
Anton von Leeuwenhoek (1674) – Studied first living cell.
Robert Brown (1831) – discovered and named Nucleus in Plant Cells.
J. Schleiden and U. Schwann (1839) – proposed first Cell Theory.
Purkinjie (1837) – named the Living matter of the Cell as Protoplasm.
Virchow (1855) – presented idea that all cells arise from pre-existing cells. (Omnis cellulae a cellula)
Types of Cells
All living organism can be classified into following two types –
Non-Cellular Organisms
-
- which do not contains any cell in their body Organisation.
- Eg. – Viruses
Cellular Organism
-
- They contains one or many cells in their body structure.
- Eg. – Bacteria, Plants and animals etc.
- They can be further classified into –
- Prokaryotic Cells
- Eukaryotic Cells
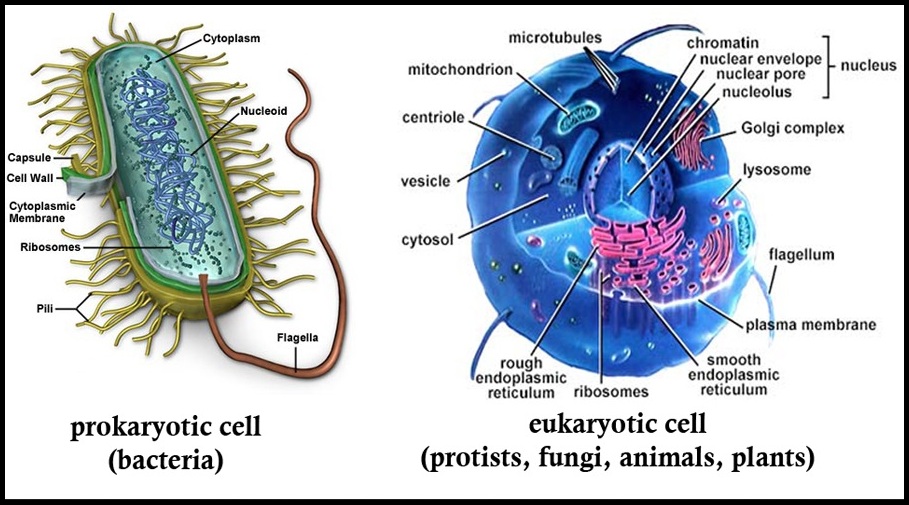
A. Prokaryotic Cells
-
-
-
- Primitive and incomplete cells.
- In these cells, Nucleus is without Nuclear Membrane. Hence, all the genetic material is directly in contact to cytoplasm.
- Fully developed cell organelles are absent. Eg. – Mitochondrion.
- Examples includes – Bacteria, Cyanobacteria etc.
-
-
B. Eukaryotic Cells
-
-
-
- Advanced and Complete Cells.
- Well defined Nucleus is Present bounded by Nuclear Membrane.
- Fully Developed Cell Organelles.
- Example includes – animals and plants etc.
-
-
Difference b/w Prokaryotic cell and Eukaryotic cell
|
Character |
Prokaryotic Cells |
Eukaryotic Cells |
Cell Size |
Generally Small |
Generally Large |
Nucleus |
No well defined Nucleus, Nuclear Membrane Absent |
True Nucleus, Nuclear Membrane Present |
Nucleolus |
Absent |
Present |
Genetic Material |
Contain one or more molecules of DNA |
Contains in form of Chromosomes which contains DNA |
Cell Organelles |
Mitochondria, Golgi Bodies, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Lysosomes Absent |
All cell organelles are well developed and Present |
Cell Wall |
Thin |
Thick (in case of Plant cell, absent in Animal Cell) |
Cell Division |
By Fission or Budding (No Mitosis) |
By Mitosis or Meiosis |
Cell Shape
- Basic Shape of the cell is spherical but the shape of the cell is ultimately determined by the function of the cell.
- Shape of the cell may be Variable or fixed.
- Variable shapes occurs in cells such as Amoeba, Leucocytes etc.
- Cells may have diverse shape such as –
-
- Polyhedral ,
- Spherical – Eg. Eggs of many animals,
- Spindle shaped – Eg. Smooth muscle fibre
- Elongated – Eg. Nerve cells, Cardiac Cells,
- Branched – Eg. Chromatophores or pigment cells of Skin,
- Discoidal – Eg. Erythrocytes and so on.
-
Cell Size
- Size ranges
- The size varies from very small bacteria (o.2 to 5 µm) to very large eggs of Ostrich (18 cm)
- The Prokaryotic cell ranges between 1 to 10 µm.
- The Eukaryotic Cell ranges between 10 to 100 µm.
- Size of the cells of unicellular organism is larger than the multicellular organism
- Smallest cell are Mycoplasma gallisepticum with size of 0.1 µm.
Cell Volume
- The cell volume remains fairly constant for a particular type of cell.
- Cell volume is independent of the size of an organism.
- The difference in total mass of the organism depends on the number of cells present in the organism not on the volume of the cell.
Cell Number
- On the basis of Cell Number, organism can be classified as –
1. Unicellular Organism – Organism which contains only one cell eg. Bacteria etc
2. Multicellular Organism – Organism which contain more than one cell.in higher animals the number may go upto in trillions.
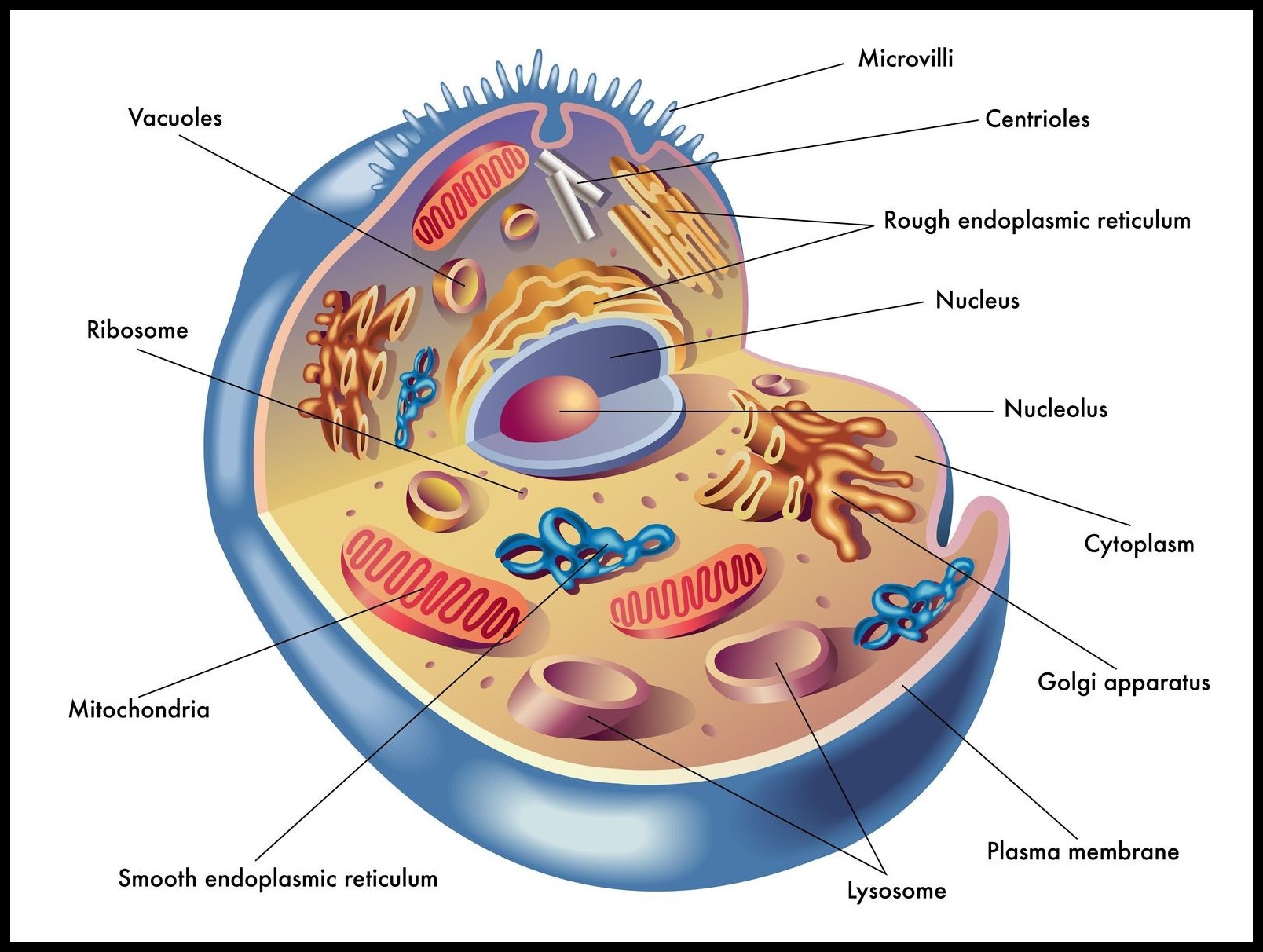
Structure of Cell
- Besides the difference in shape, size and activities, all the cells have three basic components which are –
-
- The Cell Membrane or Plasma Membrane and Cell Wall (in Plant Cells only)
- The Nucleus
- The Cytoplasm with Cytosol and Cell Organelles
-
- The Outer membrane of the Cell is called Plasma Membrane.
- Inside the Plasma Membrane, lies the Cytoplasm in which various cell Organelles and Nucleus is suspended.
- All the Functions of the Cell is performed by these cell Organelles.
So, this was all about the Fundamental unit of Life – The Cell and Prokaryotic cell and Eukaryotic cell.
In the Next Post (Click Here), we will discuss about the Structure and Organelles of the Cell.




Easy language short notes thank you loved it…