Geography
Natural Vegetation of India – Forest Products & Problems
Natural Vegetation of India – Forest Products, Problems
Table of Contents
Forest Products
- Forest Products are Major natural resource of India.
- The forest products of India can be classified into two categories –
-
- Major Products and
- Minor Products.
-
1. Major Forest Products
-
- Consists of Timber, Smallwood and Fuelwood including Charcoal.
- Indian Forest produces about 5000 species of wood of which 450 are commercially valuable.
- Both Hardwood and Softwood are obtained.
-
- Hardwood includes – teak, Mahogany, Logwood, Iron-wood, Ebony, Sal, Greenheart, Kikar, Semal etc. These woods are used for furniture, Wagons, tools etc.
- Softwood includes – Deodar, poplar, Pine, Cedar, Balsam, Fir etc. They are used for constructional timbers. They are light, strong, durable and easy to work.
-
- Provides raw material to paper industry for making paper pulp.
- They meet about 40% of energy needs of the country, of which 80% is of rural areas.
2. Minor Forest Products
-
- It includes all products obtainable from the forest other than wood i.e. which are of animal and vegetable origin.
- Some of the Minor Forest products are as follow –
a) Grasses, Bamboos and Canes as Forest Products
-
- Different types of Grasses grow in different parts of country, some of which are used as Fodder for animals.
- Grasses like Sabai is used as basic raw material in paper Industry. It is a perennial grass which grows in Bihar, Odisha, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh and western parts of Himachal Pradesh.
- Roots of Khus grass is used for making cooling screens.
- Munj is used for making Chicks, Stools and chairs etc.
- Bamboo, which grows like a tree, but is a grass may attain a height of as much as 30 m. About 100 species of Bamboo grows in Indian Forests.
- Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh and Karnataka are the main area of its growth.

-
- Bamboo also known as Poor Man’s Timber is a cheap material which is used for flooring, walling, roofing, matting, Basketry, cart hoods etc.
- Bamboos are also used for making Paper pulp for production of newspaper.
- Cane grows abundantly in moist forest of Andaman and Nicobar Island, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Kerala, Maharashtra, Nagaland, Manipur, Arunachal Pradesh and Manipur.
- It is mainly used for making strings, ropes, mats, baskets, furniture, sports goods etc.
b) Tans and Dyes as Forest Products
-
- Tannins are secretion products of plant tissues which is used for tanning leathers.
- Most commonly used Tanning materials are Mangrove, Amla, Oak, Anwal, Wattle, Ratanjot, Babul etc.
- Some of the important dyes are obtained from red Sander (Bright red), Khair (Chocolate), Flowers of Palas, bark of wattle etc.
- About 2 lakh tonnes of tans and dyes is produced in India every year.
c) Oils as Forest Products
-
- Several types of plants and trees contains various types of oils which are used for manufacturing of soaps, cosmetics, confectioneries, pharmaceutical preparations etc.
- Commercially important oils are obtained from Sandalwood, Lemongrass, Khus and Eucalyptus.
d) Gums and Resins as Forest Products
-
- Gums are obtained from stem or other parts of different trees by injury to the bark from which the liquid oozes out which solidifies as Gum.
- Most important Gum is Karaya obtained from Sterculia urens or S. villosa trees of dry deciduous forest. It is used in textiles, cosmetics, confectionary, medicines, inks etc.
- Madhya Pradesh followed by Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat and Karnataka are important producers.
- Large portion of Indian Gums are exported to USA, UK and France.
- Resin is obtained from Chir pine which grows in Himalayan regions in Arunachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Himanchal Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir.
- Resin is important raw material for several industries such as paper, paint, varnish, soap, rubber, water proofing, phenyl, plastics, oils, adhesives, greases etc.

e) Fibres and Flosses as Forest Products
-
- Fibres are obtained from tissues of the trees.
- Most of the fibre are coarse and are used for rope making. Fibres of Ak is used for making fish nets as they are fine, strong and silky.
- Flosses are obtained from certain fruits and used for stuffing pillows, mattresses etc.
f) Leaves as Forest Products
-
- Tendu leaves are used for making Bidis.
- Tendu trees grows in Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Rajasthan and Karnataka.
- Tendu leaves and Bidis are exported to Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and some other Asian and African countries.
- Leaves of Bauhinia vahlii are converted into plates and cups and are also used as wrappers.

g) Drugs, Spices and Poisons as Forest Products
-
- Different types of Drugs are obtained from different types of trees.
- Quinine is the most important drug obtained from Indian forests.
- Species, used to add aroma and flavour to food, are also obtained such as Dalchini or Cinnamon, Cardamom etc.
- Some poisons such as Strychnine, Aconite, Datura, Ganja etc. are also obtained from the forests.
h) Edible Products as Forest Products
-
- Various edible products such as fruits, flowers, leaves or roots are also obtained.
- Fruits – Mango, Bel, Jamun, Phalsa, Sitaphal etc.
- Kernels – Cashew nuts, Walnuts, Chilgoza and Kimal.
- Vegetables – Kaith, Mushrooms, Zimikand, Guchchi etc.
- Tejpatta a type of spice leaf is also obtained from forests.
i) Animal Products as Forest Products
-
- Lac is most important animal product obtained from forests. It is obtained as a secretion of insect (Laccifer lacca) which feed on the sap of trees such as plash, kusum, gular, Sal, banyan, ber etc.
- India holds the monopoly in the production of Lac. Main producing states are – Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, West Bengal, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha and Assam.
- Main Exporters includes – USA, UK, Russia and Germany.
- It is widely used in Medicine, plastics, electrical insulation, dyeing silk, Bangles making, paints, wax etc.
- Other animal products includes Honey, Wax, Silk, Moths, Horns and Hides of dead animals, ivory, antlers of deer etc.
Indirect Uses of Forests
- The indirect uses of forest can be describes as follow –
a) Prevention and Control of Soil Erosion
-
- Forest helps and plays a significant role in prevention of soil erosion by water and wind.
- The most effective way of checking soil erosion is to stop reckless cutting of forests and to plant more trees.
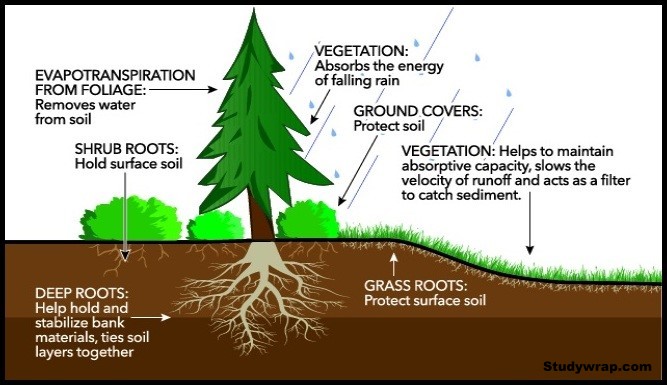
b) Flood Control
-
- Roots of the trees absorb much of the rain water and use it slowly during dry season.
- Hence, they regulate the water flow and control floods.
- The forest cover acts as a Rain-holder and a rain banker.
- In the absence of forests, the increased runoff after heavy rains along with the silt, can causes devastating floods.
c) Checks on spread of Deserts
-
- By the help of the strong winds, the sand particles are blown away from the deserts to other places which results in spread of desert.
- The roots of trees and plants binds the sand particles and do not permit its transportation by wind.
- Forest also helps in adding humidity to atmosphere and further helps in checking of the spread of desert.
d) Increase of Soil Fertility
-
- Fallen leaves of the trees add humus to soil after its decomposition which increases the fertility of the soil.
e) Effect on Climate
-
- Forest improves the extremes of the climate by reducing the heat in summer and cold in winter.
- They also influences the rainfall by lowering the temperature of moisture laden winds and increasing the relative humidity of air through transpiration.
Problems of Indian Forestry
a) Inadequate and Dwindling Forest Cover
-
- The forest cover in India is only 21.34% against the required average of 33% under the National Forest Policy 1952.
- This small percentage of forest cover has increased threats due –
-
- Growing demand for agricultural land.
- Increasing demands of major and minor forest products.
- Urbanisation and industrialisation
- Construction of multipurpose projects
- Commercial activities like mining, quarrying, oil extraction, orchard development etc.
- Shifting cultivation – Increasing pressure of population has reduced the jhum cycle to only 5 years in many parts of Nagaland, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Tripura and Manipur. Consequently, the forests do not have sufficient time to regenerate.
- Overgrazing by cattle
-
- The states of Punjab, Haryana and Rajasthan have less than 5% of their areas under forests.
b) Nature of Forests & Uneconomic utilisation of forests
-
- Most of the forests are not gregarious i.e. usable plants not growing close enough. This creates a problem in their exploitation.
- 40% of the total forest area is inaccessible while some of the forests are very thin and comprises of thorny bushes.
- Lumbering, transport and sawing of timber is still done by primitive techniques.
- Lack of scientific techniques of growing forests. Only natural growth of forests takes place in India.
c) Low Productivity
-
- Productivity of Indian forest is only 0.5 m3 / hectare while that of USA is 1.25 m3 / hectare, 1.8 m3 / hectare in Japan and 3.9 m3 / hectare in France.
d) Lack of Transport Facilities
-
- About 16% of Indian Forest is inaccessible and does not have proper transport facility.
- All weather roads and railways in forest areas are highly lacking.
- Water transport also have limited scope.

e) Forest Fires
-
- Large tracts of vegetal cover are destroyed every year by forest fires which are most destructive in dry season.
- Insufficiency of trained personnel to prevent and fight fires is a biggest problem.
f) Plant diseases, pests, insects
-
- Large parts of the forest covers suffers from plant diseases, insects and pests which leads to considerable loss of forest wealth.
- We are using primitive methods of hiring the tribal to catch and kill the insects.
g) Lack of Commercial forest
-
- Commercial forests are badly lacking. Growing awareness about environmental degradation has forced us to look at wealth as a protective agent for environment rather than treating it as commercial commodity.
h) Lack of Scientific Techniques
-
- Only natural growth of forests takes place in India whereas in many developed countries new scientific techniques are developed to fasten the tree growth.
i) Undue Concessions to Tribal and Local People
-
- Tribal and local people have been granted customary rights and concessions for free grazing as well as removing timber fuel and minor forest products.
Remedies for the Problems of the Forests
-
- Intensive development schemes for afforestation should be adopted. High yielding varieties should be used.
- Improved techniques for logging and extraction should be used.
- Proper transport facilities to inaccessible forest areas.
- Saw mills should get uninterrupted power supply.
- Latest techniques of seasoning and preservation are necessary to avoid wastage.
- Proper arrangements to save forests from fires and plant diseases can go a long way to solve several problems.
- A thorough inventory of forest resources is necessary to make an accurate assessment of our forest resources and make plans for the proper uses.
- Shifting cultivation should be discouraged and tribal depending on this type of cultivation should be provided with alternate sources of livelihood.
- People associated with forest protection should be properly trained.
So, this was all about the Natural Products, Problems & Remedies of Natural vegetation of India.
In the next post (Click Here), we will learn about the Forest Conservation in India.

