India – Location, Neighbouring Countries and land frontiers
India – Introduction
“So far as I am able to judge, nothing has been left undone, either by man or nature, to make India the most extraordinary country that the sun visits on his rounds. Nothing seems to have been forgotten, nothing overlooked.”
– Mark Twain in ‘Following the Equator’
Table of Contents
India – The Magical Country
- India is located in South Asia and is officially known as the Republic of India.
- India accounts 2.4% of total surface area of the world. India, Seventh largest country of the world, has great geographical extent. Comprising a total area of 3,287,263 sq. km, India has an estimated population of 1,293,057,000, making it the world’s second most populous country.
- India belongs to Asian continent. It belongs to South Asia and is separated by Himalayas from rest of the continent.
- Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Seaon the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the northeast; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east.
- In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lankaand the Maldives, while it’s Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand and Indonesia.
- Indian subcontinents get plenty of sunshine and monsoon rainfall, these two important climatic factor results in vastness and diversities and hence India is considered as subcontinent as it possesses all the characteristics of continent.
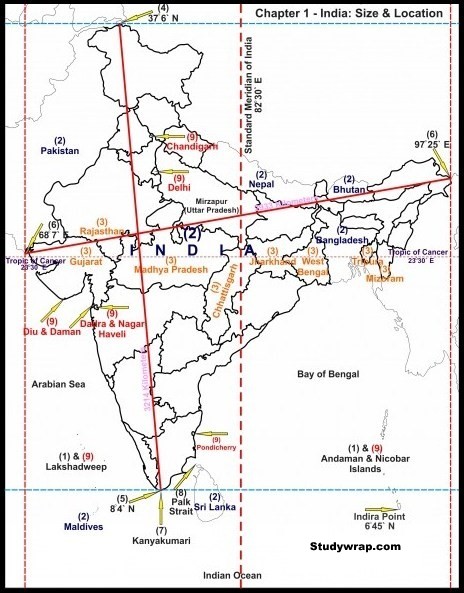
Geographical Facts about India
| location | India lies to the north of the equator in the southern Asia |
| geographical extent | · The Indian mainland
· Latitude – 8° 4′ north to 37° 6′ north latitude · Longitude – 68° 7′ east to 97° 25′ east longitude · Locational Extent – 8° 4′ N to 37° 6′ N latitude and 68° 7′ E to 97° 25′ East longitude. · India’s territorial she is 12 nautical miles from the main coastline. India has absolute rights to use this area our Southern boundary extends up to latitude and Bay of Bengal. |
| coastline | · 7517 km including the mainland the coastlines of Andaman and Nicobar Island in the Bay of Bengal and Lakshadweep Island in Arabian Sea.
· Gujarat has largest coastline followed by Andhra Pradesh Goa has smallest coastline. |
| area | · India measures 3214 km from north to South
· 2933 km from east to west · with total area of 32 87 263 square km · Rajasthan is the largest and Goa is the smallest. |
| Bordering countries | · Afghanistan and Pakistan in the Northwest.
· China Bhutan and Nepal in the north. · Myanmar in the east. · Bangladesh in the east of West Bengal. · Sri Lanka is separated from India by a narrow channel of sea formed by Palk Strait and Gulf of Mannar. |
Southernmost point – Pygmalion Point or Indira Point is located at 6° 45′ N latitude.
Northernmost point – Indira Col
Easternmost point –
Westernmost point –
The Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of the country dividing it into two latitudinal halves. It passes through 8 Indian States which are:
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Gujarat Gandhinagar-23′23
- Rajasthan Banswara-23′30
- Madhya Pradesh Bhopal-23′16
- Chhattisgarh Ambikapur-23′13
- Jharkhand Ranchi-23′34
- West Bengal Durgapur-23′52
- Tripura Nutan Bazar-23′42
- Mizoram Sabual-23′48
-
-
-
-
-
Time Difference in India
- The latitude extent of India is 68° 7′ east to 97° 25′ East longitude. Thus, the longitudinal difference between East and West is about 30 degree.
- The earth moves around its Axis through 360° in 24 hours. Thus, 1° longitude will make a difference of 4 minute in time.
- Therefore, the total difference of local time between westernmost point and easternmost point is about 120 minutes or 2 hours.
- This difference in time might create confusion in air and rail timings and so many other things across the two states.
- To avoid this confusion, 82°30′ East longitude is taken as the Standard Time Meridian of India and its local time is taken a standard throughout the country.
- It passes through Naini in Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh.
India, Tropical or Temperate Country?
Temperate part of India which is north of Tropic of Cancer is twice the area of tropical part but India has always been a tropical country for the following reasons:
1. Physical
-
-
- In the North, we have Himalayas which separate India from rest of Asia.
- Tropical monsoon dominates the climate and temperate air masses are restricted by Himalayas.
- South of Himalayas is tropical from climatic point of view; although night temperatures in winter at several places in North India may come down to the level of those in temperate lands, yet clear skies and intense insolation raise the day temperatures to the tropical level.
- Outside Himalayas everywhere agriculture is tropical in type.
-
2. Cultural
-
-
- Settlements, agricultural activities, economic activities, festivals etc are tropical in nature.
-
India and its Neighbours
India has 15106.7 Km of land border running through 92 districts in 17 States and a coastline of 7516.6 Km [6100 km of mainland coastline + coastline of 1197 Indian islands] touching 13 States and Union Territories.
| Name of the Country | Length of The Border |
| Bangladesh | 4,097 kilometres (2,546 mi) |
| Bhutan | 600 kilometres (370 mi) |
| China | 3,380 kilometres (2,100 mi) |
| Myanmar | 1,643 kilometres (1,021 mi) |
| Nepal | 1,758 kilometres (1,092 mi) |
| Pakistan | 3,323 kilometres (2,065 mi) |
| Afghanistan | 80 kilometres |
Hence, from above table we can see India shares its longest border with Bangladesh and shortest with Afghanistan.
Land Frontier’s
Border with China
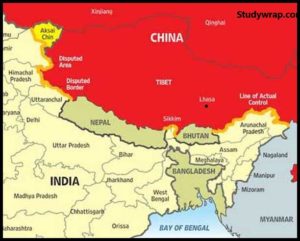
-
- 3917 km long
- Second longest border of India
- Five Indian states namely Jammu Kashmir Himachal Pradesh Uttarakhand Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh touch the Indian boundary with China
- The sino-indian border is generally divided into three sectors namely:
1. The Western Sector
-
-
- 2152 km long
- Separate Jammu and Kashmir State of India from the sinkiang province of China.
- The Western Sector boundary is the outcome of British policy towards the state of Jammu and Kashmir.
- China claims Aksai Chin district, changmo Valley, Pangong Tso and Sponggar Tso area of North East Ladakh as well as strip of about 5000 sq. km down the entire length of eastern Ladakh.
- China also claims a part of Hua Gilgit area in north Kashmir which is seeded 28 in 1963 by Pakistan.
-
2. The middle sector
-
-
- 625 km long
- Runs along the watershed from Ladakh to Nepal two Indian state Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand touch this border.
-
3. The Eastern sector
-
-
- 1140 km long
- Runs from Eastern limit of Bhutan to the point near Talu pass at the tri junction of India Tibet and Myanmar this line is also known as Mac Mohan line.
-
Border with Nepal
-
- 1758 km long
- Starts from tri junction of Nepal, Tibet and Uttarakhand in the west to Sikkim state of India in the East.
- 5 states of India, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal and Sikkim touch the Nepalese border.
- Border runs along Shiwalik Range of Himalaya
Border with Bhutan
-
- 587 km long
- Act as buffer state between India and China.
- Peaceful border with no disputes.
Border with Pakistan
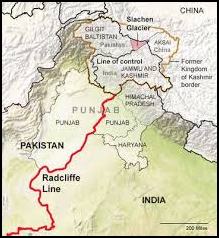
-
- 3323 km long
- Also known as Red Cliff line.
- It is the result of partition of country in 1947 by Sir Cyril Radcliffe.
- Jammu and Kashmir, Sir Creek and Siachen Glacier dispute are some major disputed regions with Pakistan.
Border with Bangladesh
-
- 4096 km long
- Longest border and accounts nearly 27% of total land border of India.
- Five Indian states namely West Bengal, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram share the border with Bangladesh.
- The boundary between India and Bangladesh determined under the Radcliffe award which divided the erstwhile Bengal province into two parts.
- Some major problems between India and Bangladesh includes refusal of transit facility to India by Bangladesh and some land disputes
Border with Myanmar
-
- 1458 km long
- Runs from India China Myanmar tri junction in the north 2010 of Mizoram.
- It runs along the watershed between Brahmaputra and Ayeyarwady.
- Indian states which touches the border Arunachal Pradesh Nagaland Manipur and Mizoram.
Water Frontier’s
Border with Sri Lanka

-
- India and Sri Lanka are separated from each other by a narrow and shallow sea called Palk Strait.
- Dhanushkodi on the Tamil Nadu coast in India is only 32 km away from Talaimanar in Jaffna peninsula in Sri Lanka. These two points are joined by a group of islets forming Adam’s Bridge.
Political division of India
India is a federal union comprising 29 states and 7 union territories, for a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.
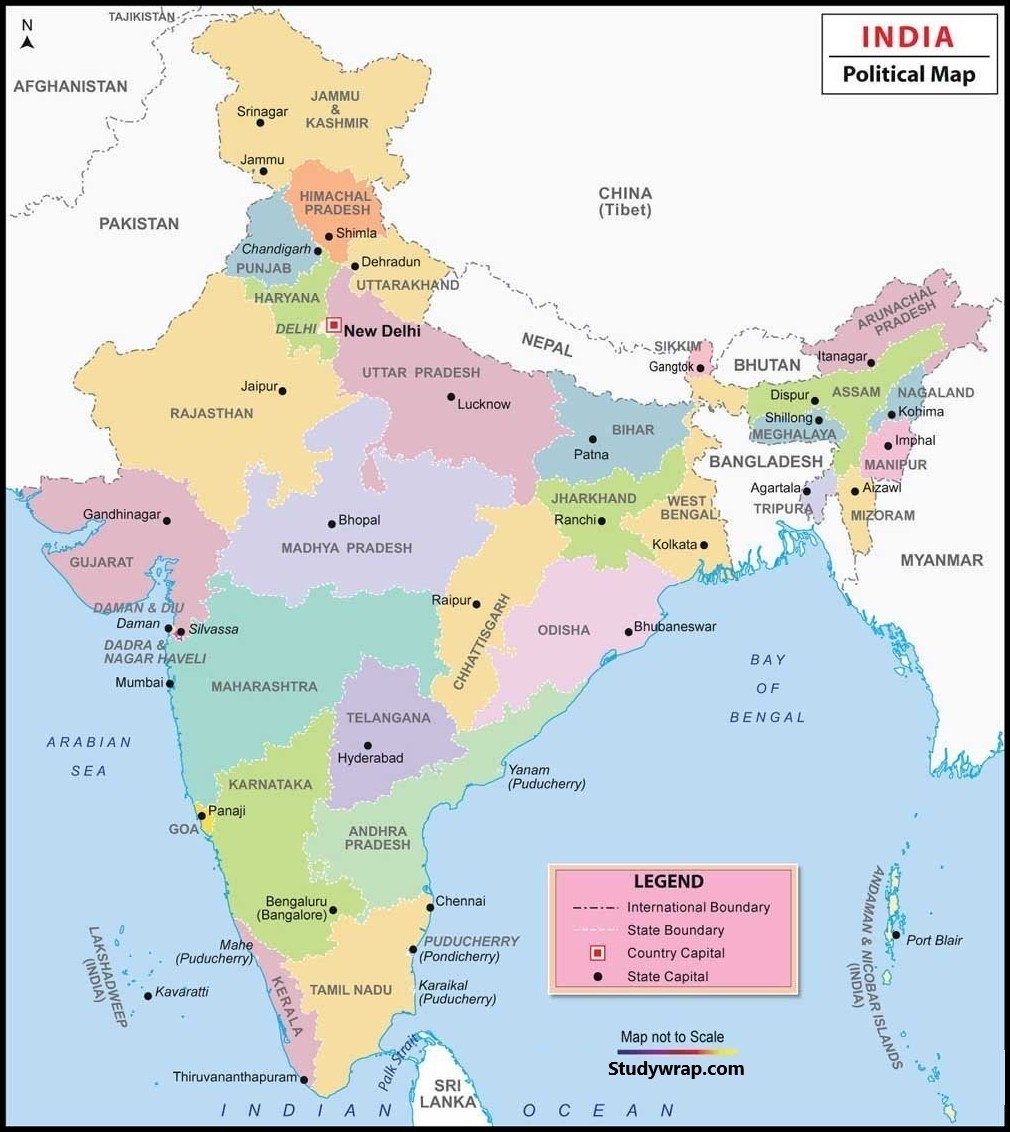
The 29 states and 7 union territories are listed below
| S.no | State | Capital |
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | Hyderabad (De jure – 2 June 2024) Amaravati (proposed) |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | Itanagar |
| 3 | Assam | Dispur |
| 4 | Bihar | Patna |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | Raipur |
| 6 | Goa | Panaji |
| 7 | Gujarat | Gandhinagar |
| 8 | Haryana | Chandigarh |
| 9 | Himachal Pradesh | Shimla |
| 10 | Jammu and Kashmir | Srinagar (summer), Jammu (winter) |
| 11 | Jharkhand | Ranchi |
| 12 | Karnataka | Bengaluru |
| 13 | Kerala | Thiruvananthapuram |
| 14 | Madhya Pradesh | Bhopal |
| 15 | Maharashtra | Mumbai |
| 16 | Manipur | Imphal |
| 17 | Meghalaya | Shillong |
| 18 | Mizoram | Aizawl |
| 19 | Nagaland | Kohima |
| 20 | Odisha | Bhubaneswar |
| 21 | Punjab | Chandigarh |
| 22 | Rajasthan | Jaipur |
| 23 | Sikkim | Gangtok |
| 24 | Tamil Nadu | Chennai |
| 25 | Telangana | Hyderabad |
| 26 | Tripura | Agartala |
| 27 | Uttar Pradesh | Lucknow |
| 28 | Uttarakhand | Dehradun |
| 29 | West Bengal | Kolkata |
| S.no | Union Territories | Capital |
| 1 | Andaman and Nicobar Islands | Port Blair |
| 2 | Chandigarh | Chandigarh |
| 3 | Dadar and Nagar Haveli | Silvassa |
| 4 | Daman and Diu | Daman |
| 5 | Delhi | Delhi |
| 6 | Lakshadweep | Kavaratti |
| 7 | Puducherry | Pondicherry |
That’s it for this introductory post on Indian Geography.
In the next post (Click here), we would study in detail the geological structure of India.

