Environment
Environment, Ecosystem, Ecotone and Niche
ENVIRONMENT
Table of Contents
ENVIRONMENT
- Everything that surrounds or affects an organism during its life time is collectively known as its environment.
- The environment is defined as the sum total of living, non-living components; influences and events, surrounding an organism.
- All organisms are essentially dependent on the other organism and environment for food, energy, water, oxygen, shelter and for other needs.
- Environment is the natural component in which biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) factors interact among themselves and with each other.

ECOSYSTEM
- A self-regulating association of living world such as plants, animals, and microorganisms, with their non-living world such as physical and chemical environment is known as ecosystem.
- This term was introduced by A.G. Tansley in 1935.
- An ecosystem can be of any size but usually encompasses specific and limited species. E.g. Aquatic Ecosystem
- Everything that lives in an ecosystem is dependent on the other species and elements that are also part of that ecological community.
- If one part of an ecosystem is damaged or disappears, it has an impact on everything else.
Benefits of Ecosystem
The direct and indirect benefits to the society from the ecosystems are given below:
-
-
-
- Ecosystems provide food, fodder, dry fruits, honey, fiber, fuel-wood, pulp, timber and manure.
- Ecosystems provide raw material to agro-based and forest based industries.
- Provide herbal medicinal plants.
- Helps in the controlling of floods.
- Mitigate temperature extremes and droughts.
- Check soil erosion.
- Add humus content in the soil and enhance soil fertility.
- Healthy ecosystems help in the purification of water, soils and air.
- Ecosystems help in the control of pests and diseases.
- Ecosystems help in maintaining the resilience characteristics of the ecosystems.
- They help in the maintenance of genetic resources.
- They promote recreation and eco-tourism.
- Forests have educational and research values.
- Forests have cultural and religious values.
- Conserve natural beauty, cultural diversity and aesthetic.
- Maintenance of genetic resources as key inputs to crop varieties and livestock breeds, medicines, and other products.
-
-
Classification of Ecosystems
-
-
-
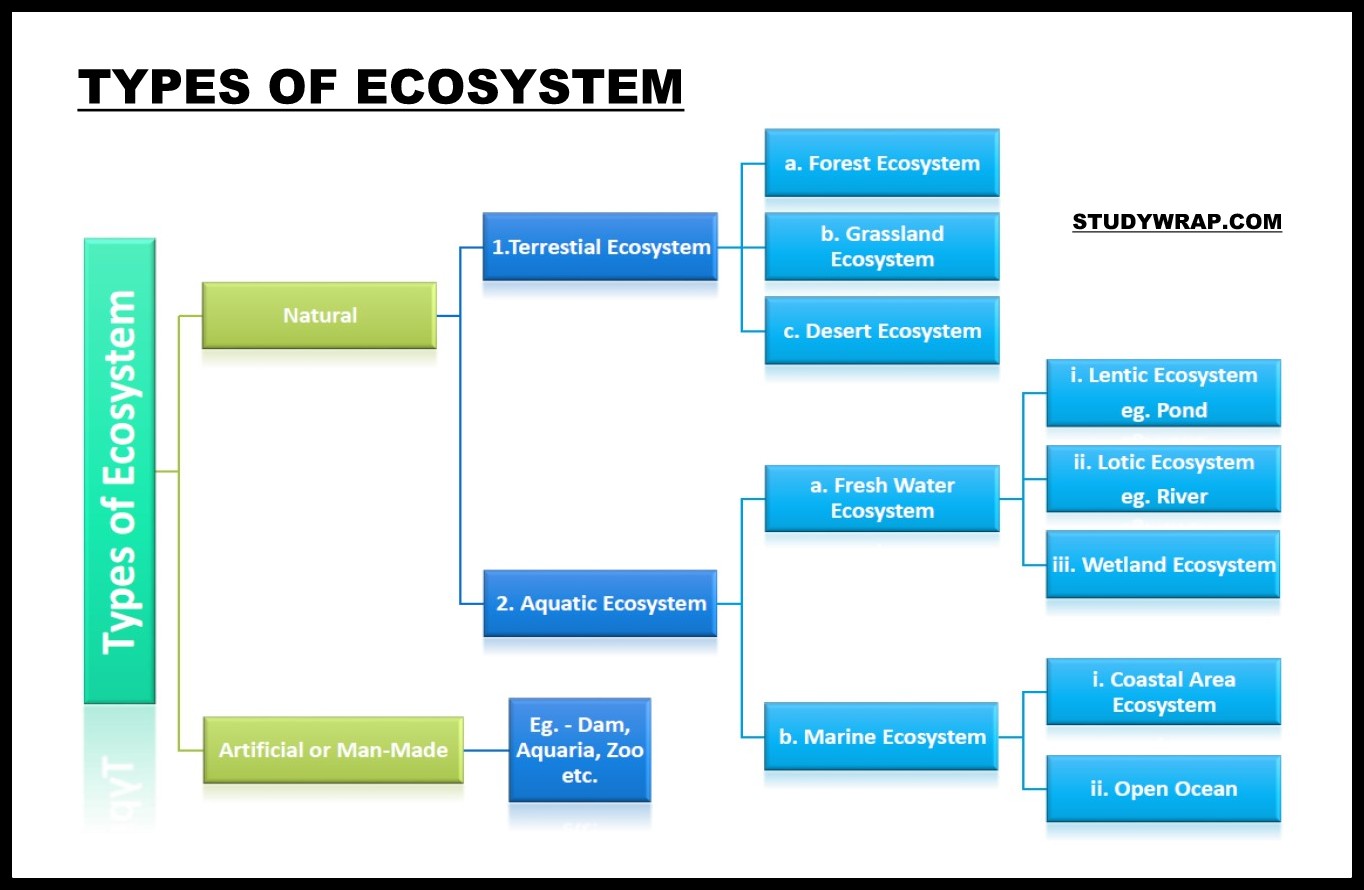
- Ecosystem is of Following Types –
-
- Terrestrial Ecosystems such as Forest, grassland and desert
- Aquatic Ecosystems such as pond, lake, wetland, river and estuary
-
- Crop fields and an aquarium are human-made ecosystems.
- Ecosystem is of Following Types –
-
-
ECOTONE
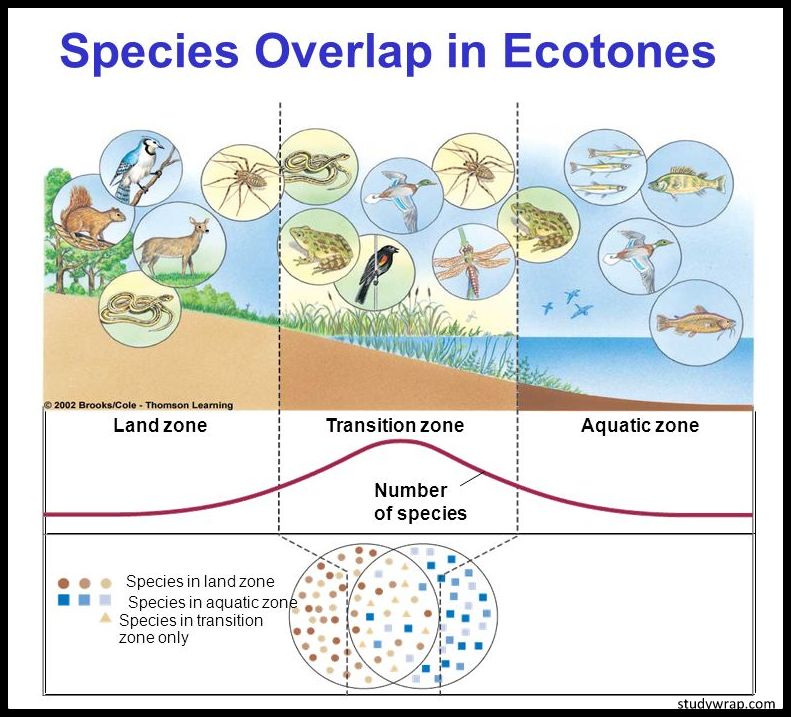
- Ecotone is a transitional area of convergence between two or more diverse ecosystems. For e.g. the mangrove forests represent an ecotone between marine and terrestrial ecosystem.
- Ecotone is the zone where two communities meet and integrate.
Characteristics of Ecotone
-
-
- They represent overlapping boundary regions or junctions where two major terrestrial or aquatic biomes meet.
- It may be very narrow or quite wide.
- It has the conditions intermediate to the adjacent ecosystems. Hence it is a zone of tension.
- It is linear as it shows progressive increase in species composition of one in coming community and a simultaneous decrease in species of the other outgoing adjoining community.
- A well-developed ecotones contain some organisms which are entirely different from that of the adjoining communities.
- Sometimes the number of species and the population density of some of the species is much greater in this zone than either community. This is called edge effect. In the terrestrial ecosystems edge effect is especially applicable to birds.
- Ecotones are usually very sensitive to climate change as well as human-induced changes. Such changes can cause variations in biodiversity, functioning, structure and species composition of an ecosystem.
-
Formation of Ecotones
-
-
- An Ecotone can basically be formed in following ways
-
-
-
-
-
- Naturally – naturally ecotones can be formed through abiotic factors such as changes in soil composition. Ecotones are very common on mountain ranges due to a wide variety of climatic conditions observed on the slopes of mountains.
- Human interaction – ecotones can also be formed as a result of human interaction. For example, the transition between areas of forest and cleared land.
-
-
-
Importance of Ecotones
-
-
- Have rich and Vibrant Biodiversity
- Has a very high density of organisms and variety of species
- Act as a bridge for gene-flow from one community to other and provide habitat to a large number of species.
- Ecotone can act as a “buffer-zone” protecting the neighbouring ecosystem from possible environmental damage.
- They are natural indicators of climate change and its consequences.
-
EDGE EFFECT
-
- Ecotones often have a larger number of species and larger population densities than the communities on either side.
- This tendency for increased biodiversity within the ecotone is referred to as the “edge effect.”
- Those species which occur primarily or most abundantly in the ecotones are called “edge” species.
NICHE
- A niche is the unique functional role or place of a species in an ecosystem.
- It is a description of all the biological, physical and chemical factors that a species needs to survive, stay healthy and reproduce.
- Niche plays an important role in conservation of organisms. A niche is unique for a species, which means no two species have exact identical niches.
Types of Niche
-
-
-
- Habitat niche – where it lives
- Food niche – what is eats or decomposes &what species it competes with
- Reproductive niche – how and when it reproduces.
- Physical & chemical niche – temperature, land shape, land slope, humidity & other requirement.
-
-
HABITAT
- Habitat is the physical environment in which an organism lives (address of an organism).
- Many habitats make up the environment.
- A single habitat may be common for more than one organism which have similar requirements.
- For example, a single aquatic habitat may support a fish, frog, crab, phytoplankton and many others.
- The various species sharing a habitat thus have the same ‘address’. E.g. Forest, river etc.
Difference between Ecology, Environment & Ecosystem
-
- Ecology is the study of interactions between organisms, organisms and the surroundings occurring within an ecosystem or environment.
- An ecosystem is a functional unit of the environment (mostly biosphere).
- An environment is a group of ecosystems.
Difference between niche and habitat
-
- A niche is unique for a species while many species share the habitat.
- No two species in a habitat can have the same niche. This is because of the competition with one another until one is displaced.
- For example, a large number of different species of insects may be pests of the same plant, but they can co-exist as they feed on different parts of the same plant.
This was all about Environment, Ecosystem, Ecotones, Niche and Habitat.
In the Next Post (Click Here), We will discuss about the Various Components of Environment and Ecosystem.
Like our Facebook Page and do share it with your friends and family. Sharing is Caring.


Great blog, thank you so much for showing us
Please provide notes pollution..!!
Awesome information, thank you kindly for your effort